
This article notes the tax incentives offered region-wise in China, including the western regions, Hainan FTP, GBA, and certain economic development zones.
China has been introducing different tax incentive schemes in certain regions. Some regions, such as the Hainan Free Trade Port (FTP) and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA), are part of the country’s economic development strategy, where tax incentives are there to help achieve ambitious development goals. Other regions are encouraged due to their lack of geographical and legacy industrial advantages and need policy support to lure investments for economic development like the vast western regions.
In this article, we present tax incentives offered in different Chinese regions. We also compare the differences and similarities of some tax preferential policies across regions.
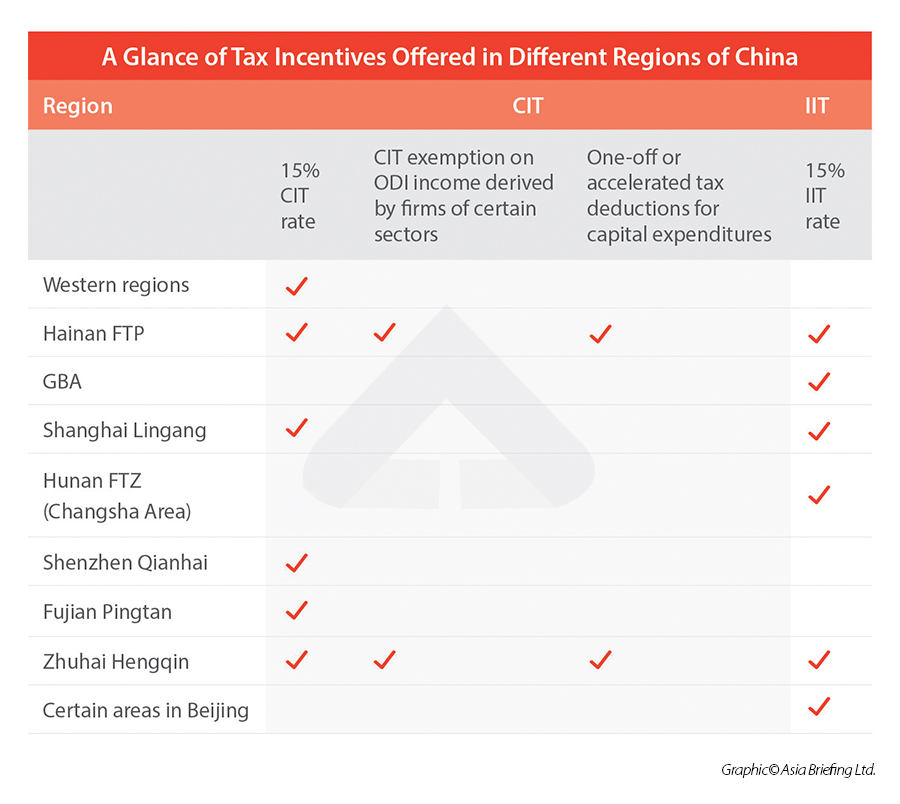
CIT cuts in Western China
Until December 31, 2030, enterprises set up in China’s western regions with their main businesses in encouraged industries of the specific region can enjoy a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 15 percent, according to MOF SAT NDRC Announcement [2020] No.23.
The western regions are Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Shaanxi, Gansu, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Yunnan, Qinghai, Tibet, and Xinjiang. Some underprivileged cities in other provinces – Xiangxi, Enshi, Yanbian, and Ganzhou – may also adopt the same CIT preferential policy.
To be eligible, the enterprise’s main business must fit into the encouraged category of the relevant industry catalogues. And its main business revenue must account for at least 60 percent of its total business revenue.
Xinjiang
To especially support the economic development of Xinjiang in Western China, a “2+3 years tax holiday” policy is available for enterprises setting up in Xinjiang’s underprivileged areas and a “5 years tax holiday” can be availed by those established in Kashgar and Khorgos.
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2030, enterprises set up in Xinjiang’s underprivileged areas whose main business is in encouraged industries can enjoy CIT exemption for the first two years (starting from the first income-generating year), and a halved CIT rate (that is, 12.5 percent) in the subsequent three years, according to Cai Shui [2021] No.27. Those set up in special economic development zones of Kashgar and Khorgos can be straightly exempt from CIT for five years (starting from the first income-generating year).

Tax incentives in Hainan FTP
China is currently putting great effort to transform Hainan island into a world-leading free trade port. To attract businesses and talents, the government has introduced a series of innovative tax relief measures. Businesses may find them very attractive when contemplating their Hainan operations.
CIT incentives in Hainan FTP
Enterprises registered in Hainan Free Trade Port get the chance to enjoy the following CIT relaxations, according to Cai Shui [2020] No.31.
CIT rate reduction
Enterprises that (a) are registered in Hainan FTP, (b) have “substantive operations” in Hainan, and (c) with their main business in the encouraged industries in Hainan are entitled to CIT at a reduced rate of 15 percent from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2024. Likewise, to qualify, the enterprise’s main business must be in the encouraged industries of Hainan, and the income from the enterprise’s main business must constitute 60 percent or more of its total income.
What’s more, during the period from 2025 to 2035, the applicable scope of the lowered CIT rate of 15 percent will be expanded to benefit all Hainan enterprises (only except those in a “negative list” sector), according to the Overall Plan for the Construction of Hainan FTP released by the State Council.
CIT exemption on overseas direct investment income
Enterprises of tourism, modern service, and high-tech sectors registered in Hainan FTP are exempt from paying CIT on income from new overseas direct investment between January 1, 2020 and December 31, 2024.
The tax exemption applies to (a) income from operating profits from newly established overseas branches and (b) dividend income that is a result of new direct investment obtained from overseas subsidiaries in which the Hainan enterprise holds a 20 percent or more equity. Plus, to enjoy the tax exemption, the foreign jurisdiction, where the overseas branch is located or investment is made, must impose a statutory income tax of five percent or more.
Accelerated tax deductions for eligible capital expenditures
Furthermore, Hainan-registered enterprises are allowed to accelerate the pre-tax deduction of the cost of fixed assets (excluding building) or intangible assets that are acquired between January 1, 2020 and December 31, 2024.
- For assets with a unit value no more than RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million), a one-off pre-tax deduction is allowed; and
- For assets with a unit value of more than RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million), accelerated depreciation or amortization is allowed.
This tax treatment in Hainan FTP is quite similar to that provided in Cai Shui [2018] No.54. However, Hainan’s accelerated depreciation/ amortization regime for eligible capital expenditure is more relaxed because the Cai Shui [2018] No.54 (which is applicable nationwide) does not cover intangible assets, but Hainan’s policy covers fixed assets (including those self-constructed and self-developed) and intangible assets. Plus, Cai Shui [2018] No.54 contains more restrictions on fixed assets with a unit value of more than RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million).
CIT and IIT reduction for venture capital enterprises
According to the 2021 Guidelines for Venture Capital in Hainan FTP, for venture capital enterprises that are established in Hainan and meet the requirements:
- 70 percent of the investment in small and medium-sized high-tech enterprises and start-up technology enterprises can be deducted from its taxable income; and
- A reduced CIT rate of 15 percent can be enjoyed for income from industries encouraged by Hainan FTP.
Moreover, qualified employees of venture capital enterprises may be exempt from paying IIT on the portion that exceeds 15 percent of their taxable incomes gained in Hainan FTP, including comprehensive incomes, business incomes, and talent subsidy income recognized by Hainan Province.
IIT incentives
According to Cai Shui [2020] No.32, qualified high-end and urgently needed talents working at Hainan FTP can enjoy a partial individual income tax (IIT) exemption. That is, the portion of the IIT exceeding 15 percent of their taxable income can be exempt during the period from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2024.
This talent policy is modeled after the one implemented in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA).
However, Hainan even has more IIT relaxation after 2024. From 2025 to 2035, Hainan FTP will limit the IIT brackets on comprehensive income and business income to 3%, 10%, and 15% percent (the normal tax brackets are: 3%, 10%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, and 45% for comprehensive income; and 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, and 35% for business income) for certain individuals residing in Hainan. To qualify, the individual must reside in Hainan for no less than 183 days a year.
Import duty exemption
Encouraged industrial enterprises producing goods originating from Hainan that do not contain imported materials or contain imported materials but with added value exceeding 30 percent after processing of imported intermediary products in Hainan are exempt from import tariffs when entering the rest of China.
Tax incentives in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao GBA
IIT incentives
In GBA, foreign high-end talents and urgently needed talents working at the nine mainland cities – namely Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Huizhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, and Zhaoqing – can apply for a financial subsidy to lower their IIT burdens from January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2023. The subsidy amounts to the portion of the IIT paid by the qualified talent that exceeds 15 percent of one’s taxable income, according to Cai Shui [2019] No.31.
IIT Incentives – Hainan vs GBA
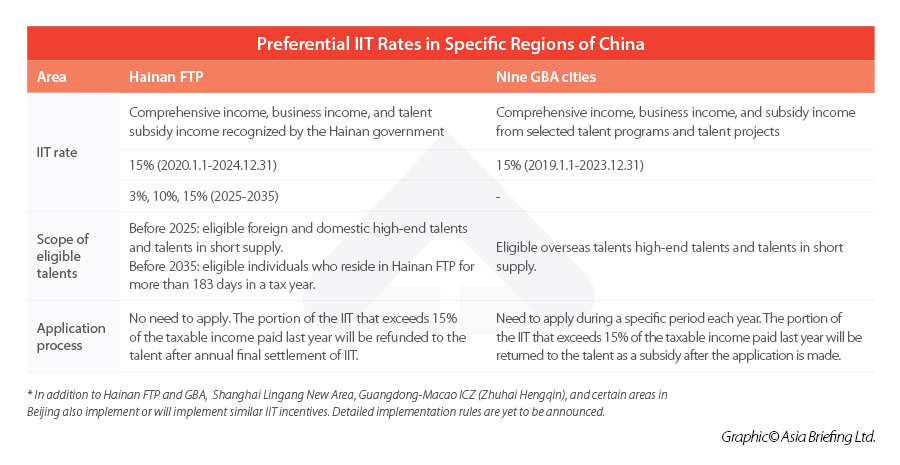
Basically, the IIT incentives in Hainan FTP and in GBA both aim to lower the actual income tax burden of qualified talents to 15 percent of their taxable income. Besides, in both policies, taxable income refers to the individual’s comprehensive income, business income, and recognized subsidy income (investment or asset transfer income is not covered).
However, there are also some differences. First, Hainan’s IIT policy applies to both foreign and domestic talents, while GBA’s IIT incentive is only applicable to foreign talents (including residents of Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan).
Second, eligibility criteria for Hainan’s IIT incentives considers social security contributions, proof of labor relationship, minimum annual income (for “high-end talents”), and the talent catalogue (for “talents in short supply”). However, in the GBA, qualification criteria vary from city to city. In addition to the basic requirements, foreign talents also need to satisfy additional criteria in their city (such as the city’s catalogues of high-end talents and talents in short supply, the minimum working days/annual income requirements, etc.).
Further, to enjoy the IIT relief, GBA talents need to file applications during a specific period each year. The excess portion of the IIT paid last year will be returned to the talent this year as a subsidy after the application is successful. However, Hainan provides a more streamlined process. Overpaid tax can be refunded to the talent immediately after the talent completes the annual final settlement of IIT
Notably, some other special economic zones, including Lingang New Area of Shanghai Free Trade Zone (FTZ), Guangdong-Macao Intensive Cooperation Zone (also known as Zhuhai Hengqin area), and Hunan FTZ Changsha Area adopt similar IIT policies.
VAT incentives
To support import and export business, the GBA has introduced value-added tax (VAT) exemption policy for some insurance companies as well as tax refund policy at port of departure.
VAT exemption for insurance enterprises
From October 1, 2020 to December 31, 2023, income of insurance premium for international shipping derived by insurance enterprises registered in Guangzhou from enterprises registered in Nansha Area of Guangdong FTZ will be exempt from VAT, according to Cai Shui [2020] No.48.
Export tax rebates
From October 1, 2020, containerized cargos to be shipped abroad from the designated 37 ports of shipment and passing through Nansha Bonded Port of Guangzhou and Qianhai Bonded Port of Shenzhen (the place of departure) by qualified export enterprises with qualified transportation enterprises as the carriers, will be eligible for the export tax rebate policy at the port of the shipment.
Tax incentives in certain economic zones
Some of China’s special economic zones like free trade zones (FTZs) also offer competitive tax incentives for companies.

Shanghai Lingang New Area
CIT incentives
Starting January 1, 2020, enterprises registered in Lingang New Area of Shanghai FTZ may be eligible for a lowered CIT rate of 15 percent for five years since its date of establishment, according to Cai Shui [2020] No.38.
To qualify, the enterprise’s main business must be in four key industries – integrated circuits (IC), artificial intelligence (AI), biomedicine, and civil aviation. And it must engage in substantive production and R&D activities in a sector listed in the Catalogue of Key Fields and Core Links of Lingang New Area.
IIT incentives
Lingang also grants financial subsidies for foreign high-end and shortly needed talents, which can lower their effective IIT rate to 15 percent. According to some public reports, the area has started implementing the relevant IIT measures, although the detailed implementation rules are not public.
VAT incentives
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2024, enterprises registered in Yangshan Special Comprehensive Bonded Zone (CBZ) of Lingang New Area are exempt from VAT on income derived from providing transportation services, handling services, and warehouse services within the zone, according to Cai Shui [2021] No.3.
Shenzhen Qianhai
CIT incentives
According to Cai Shui [2021] No.30, from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025, qualified enterprises engaged in encouraged business activities in Qianhai Shenzhen-Hong Kong Modern Service Industry Cooperation Zone are able to enjoy a reduced CIT rate of 15 percent.
Shenzhen Qianhai encourages businesses in 30 sectors under five broad industry categories – modern logistics, information services, technology services, cultural and creative industries, and commercial services.
Fujian Pingtan
CIT incentives
According to Cai Shui [2021] No.29, from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025, qualified enterprises engaged in encouraged business activities in Pingtan Comprehensive Experiment Zone of Fujian FTZ are entitled to the reduced 15 percent CIT rate.
Fujian Pingtan currently encourages 146 Industry sectors under five categories – high-tech, consumer services, agricultural and marine industry, ecological and environmental protection, infrastructure management, and tourism.
Zhuhai Hengqin (Guangdong-Macao ICZ)
In September, the State Council rolled out a masterplan for the construction of Guangdong-Macao Intensive Cooperation Zone (ICZ), which contains a series of favorable tax policies. Businesses may find many of them similar to those implemented at Hainan FTP.
CIT incentives
Eligible enterprises registered in the Cooperation Zone will be entitled to a reduced CIT rate of 15 percent on their business income. Also, CIT will be exempt on the newly added earnings from overseas direct investment into the tourism, modern services, and high technology businesses set up in the Cooperation Zone.
Further, capital expenditure of businesses that meets the criteria will be allowed a one-off deduction before tax for the taxation period in which the expenditure occurred or accelerated depreciation and amortization.
IIT incentives
The ICZ also plans a policy similar to the IIT incentives implemented at the nine Guangdong cities in GBA as well as in Hainan FTP.
Overseas and domestic high-end talents and shortly needed talents working in the ICZ may be exempt from paying the portion of income tax that exceeds 15 percent of their taxable income. Moreover, Macao residents working in the CIZ may apply Macao’s IIT rates.
Beijing IIT incentives
Eligible overseas high-end talents working in certain areas of Beijing will be able to enjoy preferential IIT policy, according to the State Council. The detailed implementation measures are yet to be announced.
Beijing Zhongguancun
CIT exemption on income from qualified technology transfer
Resident enterprises registered in Beijing Zhongguancun National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone are exempt from CIT on income derived from qualified technology transfer not exceeding RMB 20 million (approx. US$3.1 million), according to Cai Shui [2020] No.61. In addition, CIT on income from qualified technology transfer exceeding RMB 20 million (approx. US$3.1 million) can be halved.
This tax treatment shares similarities with the STA Announcement [2015] No.82, which allows resident enterprises nationwide to enjoy CIT cuts on income from qualified technology transfer. However, the STA Announcement [2015] No.82 has a smaller tax-free limit of RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million) and stricter definition of qualified technology transfer.
CIT reduction for venture capital enterprises
Furthermore, according to Cai Shui [2020] No.63, effective from January 1, 2020, for qualified corporate venture capital enterprises (CVCE) in the Demonstration Zone:
- If the gains on the transfer of equity, which has been held for not less than three years, exceeds 50 percent of the total gains on the transfer of equity in a given tax year, a 50 percent exemption for CIT based on the shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end is allowed (CIT Exemption = Shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end x CIT liability for year ÷ 2); and
- If the gains on the transfer of equity, which has been held for not less than five years, exceeds 50 percent of the total gains on the transfer of equity that year, a 100 percent exemption for CIT based on the shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end is allowed (CIT Exemption = Shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end x CIT liability for year).
This article was first published by China Briefing, which is produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The firm assists foreign investors throughout Asia from offices across the world, including in China, Hong Kong, Vietnam, Singapore, India, and Russia. Readers may write info@dezshira.com for more support.






